最近看到一篇很不錯的文章MongoDB internal Architecture,主要在描述 MongoDB Storage Engine 的演進
其中在 5.3 比較大的改變是引入了 Clustered Collection 調整了 Storage Engine 儲存的機制,這也連帶影響 MongoDB 在 Collection 上的效能表現,以下從文章中摘要 Storage Engine 演進,並透過 Benchmark 去驗證看看實際的表現
MongoDB Storage Engine 演進
MMAPv1
最一開始 MongoDB 的 Storage Engine 是 MMAPv1,採用 B+Tree 架構以 _id 為 primary key,leaf node 儲存 DiskLoc 直接指向儲存於硬碟上的位置(透過 file name + offset)
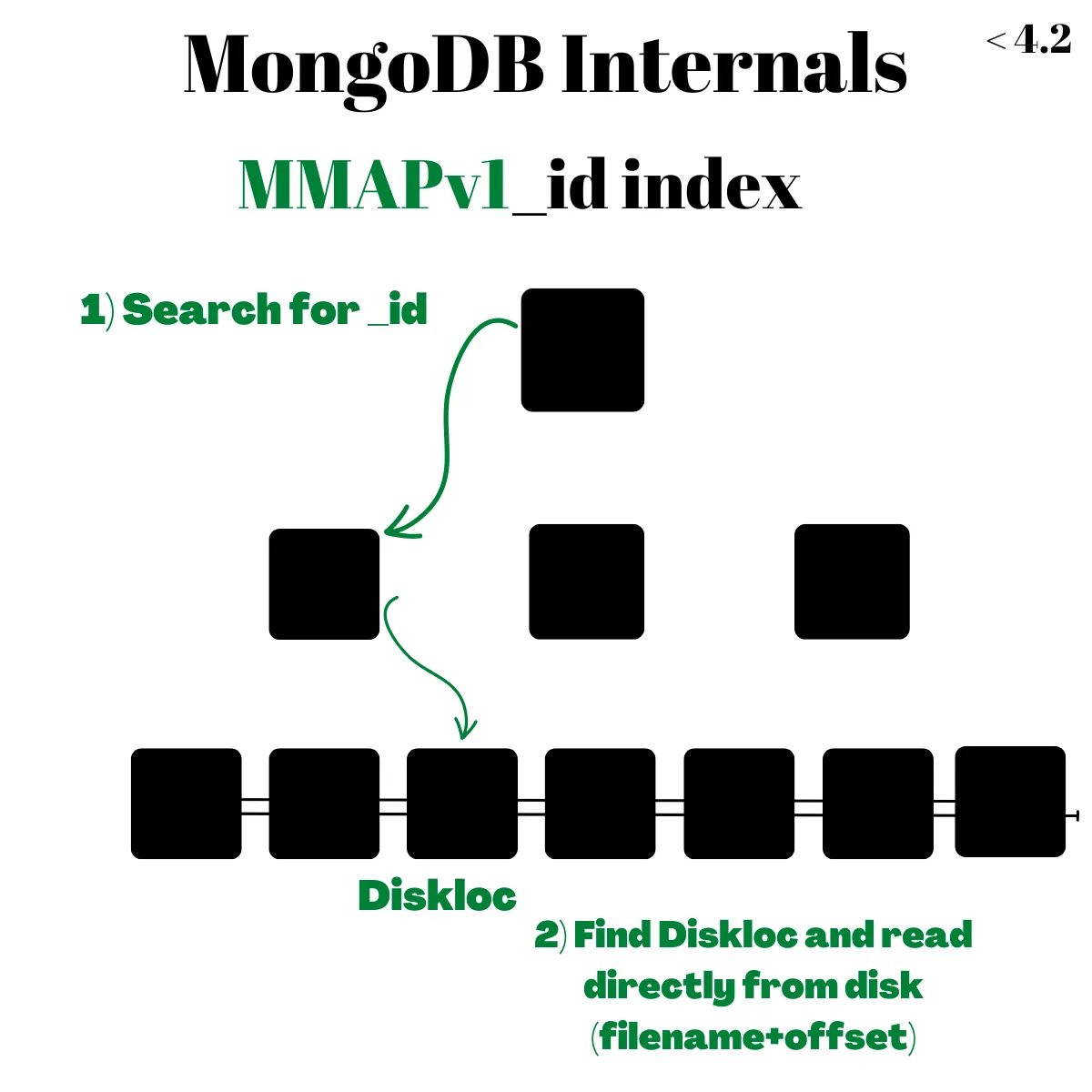
MMAPv1 的優點是查詢速度很快,只需要 O(logN) 在 B+Tree 找到 leaf node + O(1) 去硬碟讀取資料即可
但有幾個重大缺點
- 因為是儲存實際 Disk 位置,所以當
document 因為 insert / update / delete 而改變 Disk 位置時,就需要大規模的改寫 DiskLoc 造成效能的影響 - 儲存時沒有壓縮
- 一開始只提供 database level / collection level 的 lock,這也導致在 parallel 執行上效率不高
WiredTiger
MongoDB 在 2014 年收購了 WiredTiger 這個 Storage Engine,並於 3.0 加入於 3.2 變成預設的 Storage Engine
在儲存上同樣是採用 B+Tree 結構,但這時候 _id 不是 Clustered Index Key 而是在內部 WiredTiger 會自動為每個 document 設定 recordId 當作儲存排序的依據
所以 _id 跟其他 secondary index 相同,都是先在自己的 B+Tree 上查找,找到對應的 recordId 後再去 recordId Clustered Index 搜尋
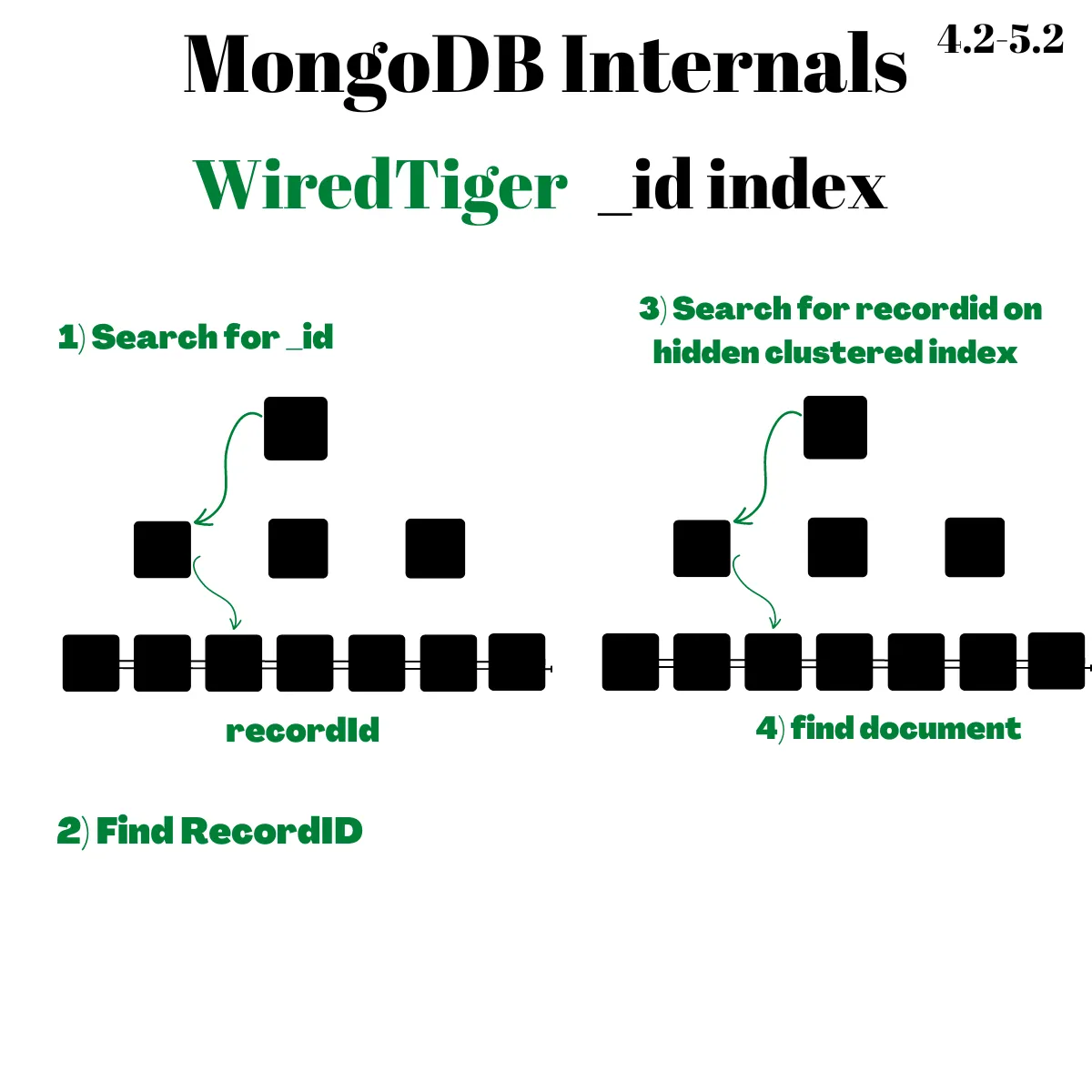
也因此 WiredTiger 的缺點是查詢變慢一些,因為需要搜尋兩次 B+Tree 才能去 Disk 撈資料
但有幾項優點
- Insert、Update、Delete 效能比 MMAPv1 穩定
- 提供 document level lock,大幅改善 parallel 效能
- 壓縮 BSON 在儲存,減少 Disk 用量代表可放進 buffer pool 的資料筆數也增加
根據這篇文章 Linkbench for MySQL & MongoDB with a cached database 的實驗可以看到 MongoDB WiredTiger 在查詢與寫入都吊打其他的 Storage Engine

有趣的是 MySQL 寫入、查詢吊打 MongoDB XD
在單機的環境下看起來老牌 RDBMS 比較厲害,只是實際選擇還需要再考量到 scalability 等狀況
WiredTiger Clustered Collection 原理
接著到了 MongoDB 5.3 的 Clustered Collection,剛剛有提到實際內部儲存依據是用 recordId 排序,那如果直接拿 _id 當作 Clustered Index 的 key 是不是就能更加速寫入跟查詢的效率?這正是 Clustered Collection 所採用的方式,直接拿 _id 當作 Clustered Index
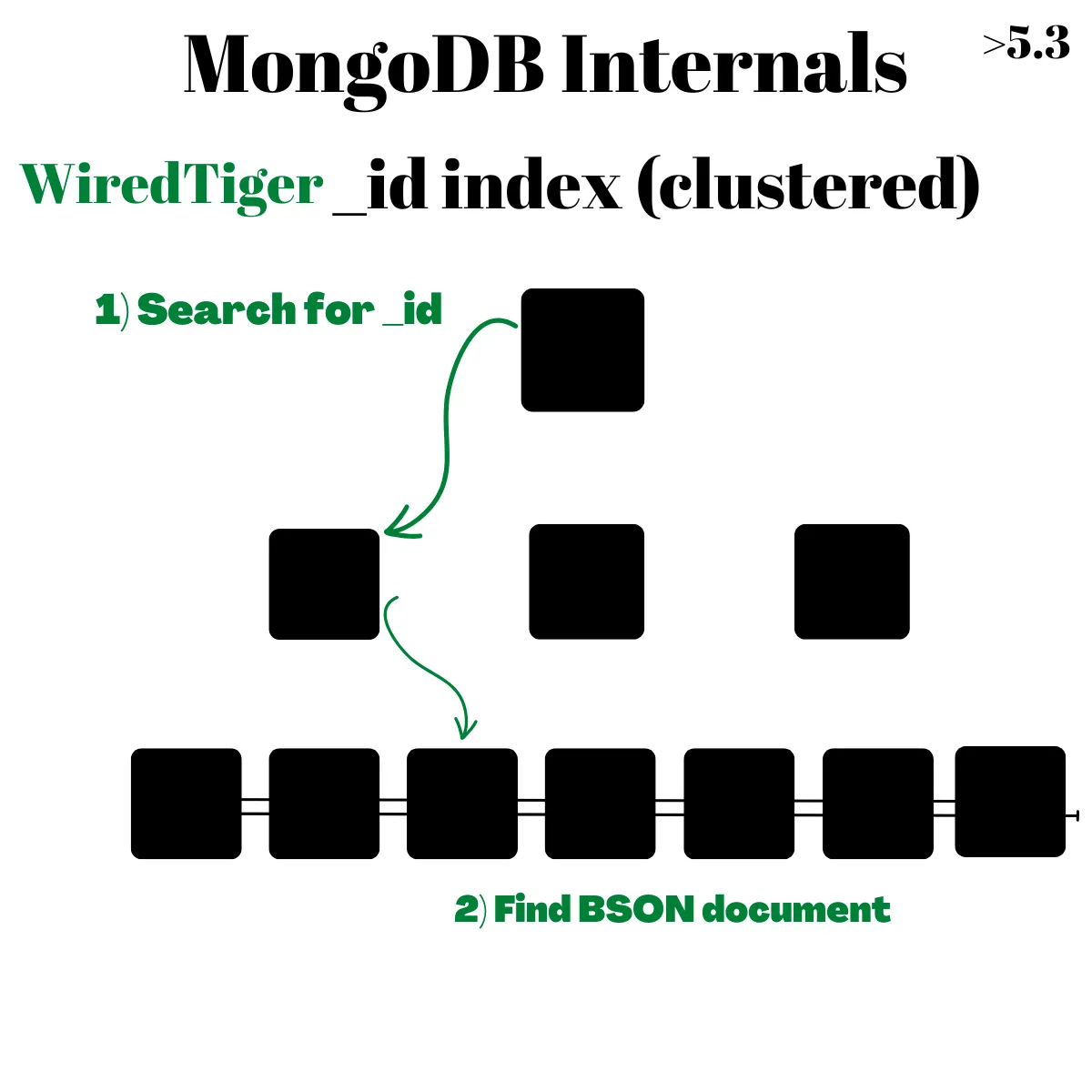
根據官方文件,在建立 Clustered Collection 就必須指定用 _id 建立,同時必須是 unique
| |
根據文件 Clustered Collections所述有幾個優點
- 大幅度增加 _id 搜尋速度,尤其是 range scan 上,因為少了一次去查找 recordId index
Faster queries on clustered collections without needing a secondary index, such as queries with range scans and equality comparisons on the clustered index key.
- 增加 CRUD 的效能
Clustered collections have additional performance improvements for inserts, updates, deletes, and queries.
但也不是全然沒有壞處
- Secondary Index leaf node 會儲存 Clustered Index 的 key,而因為前面提到原本 collection Clustered Index 是用 recordId(8byte),而 _id 預設是 12byte,所以就直接影響了 Secondary Index 的 size (增加約 20%)
_id 是用戶可以預設,如果設錯可能會讓效能變差
整體來說目前 MongoDB Clustered Collection 儲存方式有點接近 MySQL,同樣都是
- 指定 Primary Key 當作 Clustered Index 影響實際儲存的方式
- Secondary Index leaf node 指向 Clsutered Index
同樣的如果 _id 是採用 UUID 等亂序,也同樣會有效能上的影響,這部分可以參考 UUIDs are Popular, but Bad for Performance — Let’s Discuss,這點後續 benchmark 會驗證
Benchmark
透過以下幾個實驗來實際檢驗一下 MongoDB v6.0.5 Clustered Collection 的效能
- 比對 CRUD 在 Clustered Collection vs 一般 Collection 差異
預期 CRUD 在 Clustered Collection 應該要較好 - 針對 Secondary Index,比較實際大小與效能
預期 Secondary Index 在 Clustered Collection 儲存空間要比較大,如果尺寸沒有大到記憶體塞不下的狀況,效能部分預期是差不多 - _id 改用 UUID 對於寫入效能的影響
預期 Clustered Collection 會有比較差的表現,因為底層儲存結構的關係
相關程式碼在 sj82516/mongodb-bm-cluster-collection
Insert 比較
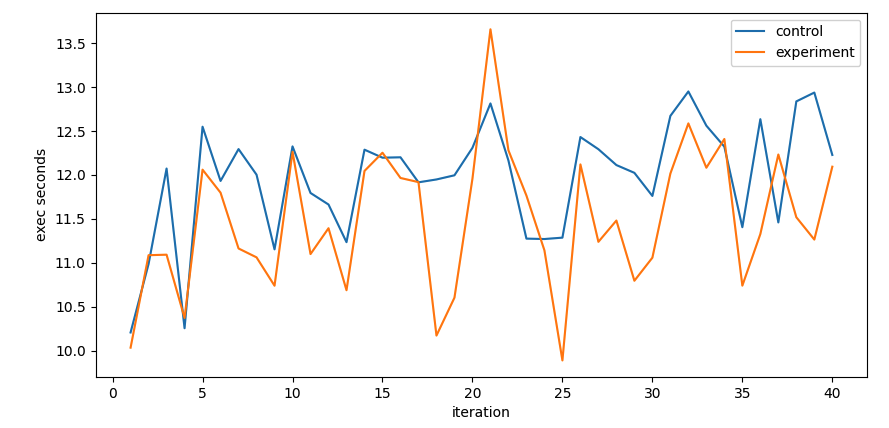
實驗每個 iteration 準備 100 萬筆資料並用 insert_many 批次寫入 1000 筆,總共插入 2000 萬筆;實驗組是 clustered collection 但對照組不是
從圖表來看 Clustered Collection 有稍微比較好但沒有到非常明顯的變化
Search 比較
測試過程有發現一個 MongoDB 的 bug Performance Issue about Clustered Collection : where there are more than one _id search condition, the search would fallback to COLLSCAN,主要是 find 條件中有多個 _id 時 index 會沒有吃到 clustered index 導致查詢非常慢
但有趣的是 secondary index 目前測試是沒有這個問題的
| |
可以看到 cluster search 慢到爆,delete_many 有同樣的 issue
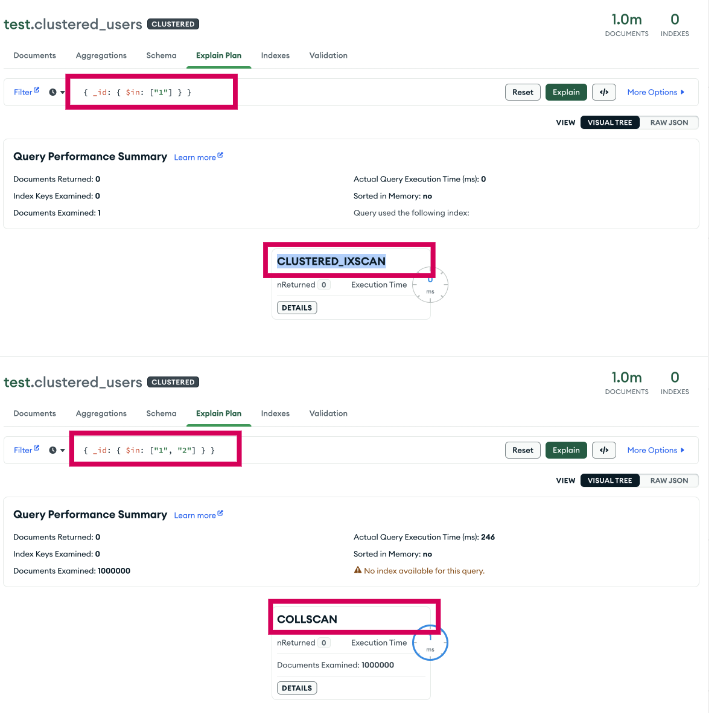 本來以為是不是 driver 問題,但實際用 Mongo Compass 官方 GUI tool 去分析查詢,確實發現只要 $in 裡面的條件超過一筆就會變成 COLLSCAN
本來以為是不是 driver 問題,但實際用 Mongo Compass 官方 GUI tool 去分析查詢,確實發現只要 $in 裡面的條件超過一筆就會變成 COLLSCAN
Secondary Index 大小
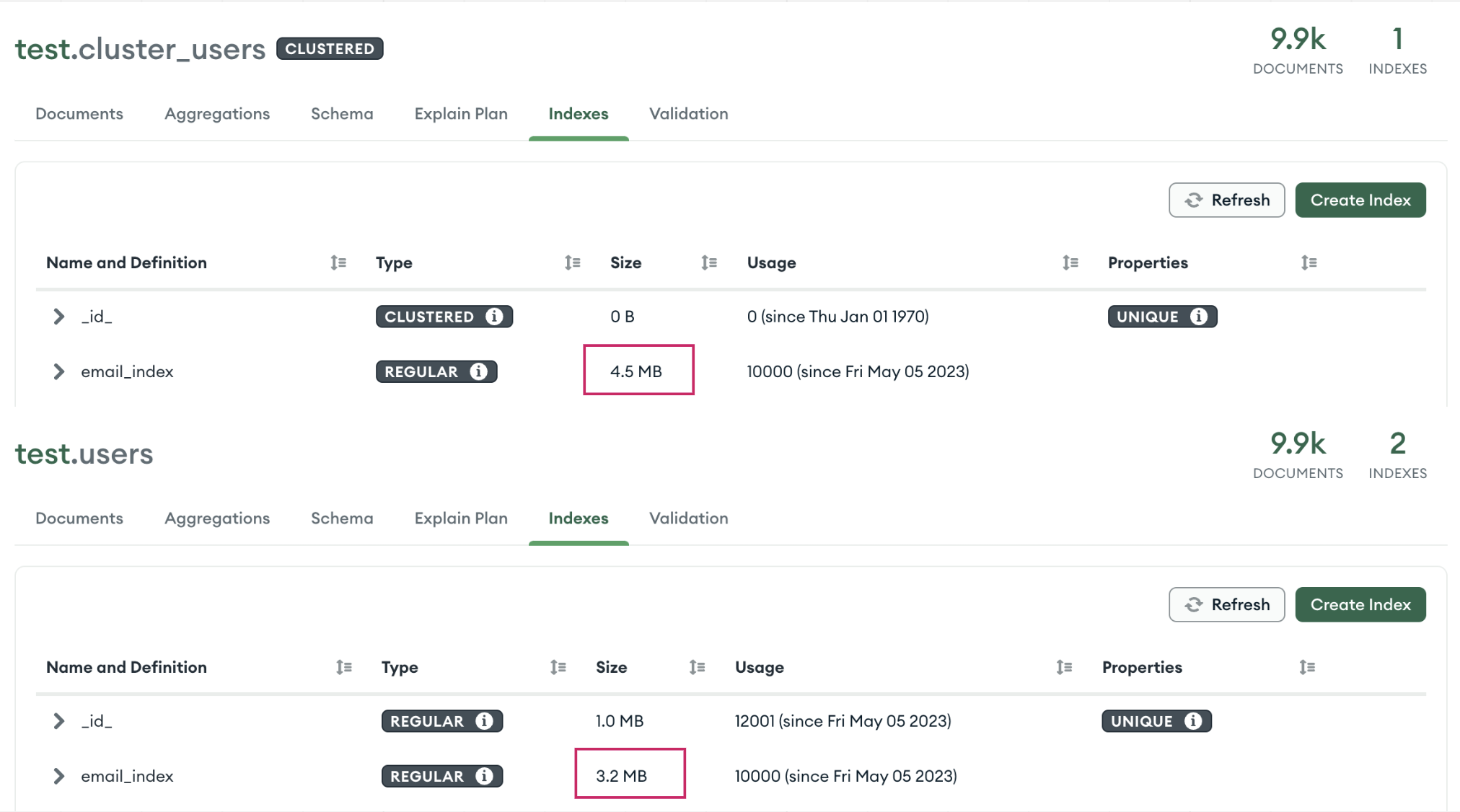
可以看出同樣的 documents 下 Secondary Index 在 Clustered Index 確實變大快 25%
UUID 寫入的影響
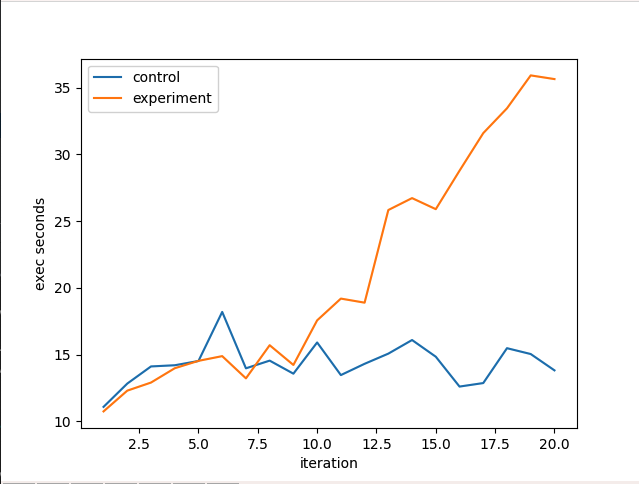
實驗每個 iteration 準備 100 萬筆資料並用 insert_many 批次寫入 1000 筆,兩個 collection 都是 clustered collection,實驗組 _id 設定為 UUID
可以看到 UUID 對於效能的負面影響十分巨大
延伸閱讀
以下是我在閱讀時想到的一些額外問題,覺得蠻有趣也順便記錄一下
為什麼 WiredTiger 一開始不支援 Clustered Index
既然有這麼大的好處,為什麼一開始不支援呢?在這個 google group discuss 有稍微帶到 Purpose of a separate index storage for primary id for MongoDB
理解起來比較像技術債,一開始 MMAPv1 是使用 DiscLoc,後來 WiredTiger 改成用 RecordId 而不是直接綁死 Disk 位置
the origin of this decision was the MMAPv1 storage engine. There, indexes would map keys to
'DiskLoc' values, containing a pair of 32-bit integers representing the file number in the database and offset in that file.Since then we have replaced DiskLoc by a RecordId that does not represent a physical location, but rather a logical document number.
另外就是 MongoDB 對於 Primary Key 使用有額外的用途,包含 Sharding,所以實作比想像中複雜 另外也有提到即使有效能上的提升但對於 Secondary Index 是有負面影響
we could gain efficiency (both time and space) by using the primary key directly to index the data. However, as MongoDB puts few restrictions on the primary key, it is common for these primary keys to have a non-trivial size.
This in turn means that all secondary indexes become less efficient. Some users have many indexes, so they'd be negatively affected by such a change.……
結語
整體來說 Clustered Collection 寫入效能確實有好上一些,搜尋部分因為有 bug 暫時還不確定,而 Secondary Index 體積會有感的變大;目前整題評估下來不建議採用 Clustered Collection,些微的效益比不上這些風險與副作用